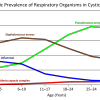
Infectious disease-related deaths of low birth weight infants, United States, 1968 to 1982
Abstract
Infant mortality rates in the United States are higher than in any other developed country. Low birth weight (LBW) is the primary determinant of infant mortality.
Despite city, state, and federal programs to prevent LBW, decreases in infant mortality in the 1980s appear to be largely secondary to improved survival of LBW infants rather than to a decline in the rate of LBW births.… Read more