The Roles of Epidemiologists, Laboratorians, and Public Health Agencies in Preventing Invasive Cronobacter Infection
Abstract
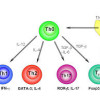
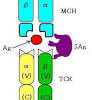
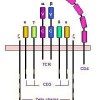
BACKGROUND: Cronobacter can cause severe, invasive infection in very young infants. These bacteria can also colonize or cause insignificant infections in immunocompromised, elderly, and/or hospitalized adults.
METHODS: This editorial review highlights key points addressed in the Frontiers Research Topic on Cronobacter, discusses the clinical presentation and epidemiology of Cronobacter infections, and examines the responses of public health agencies to this problem.… Read more